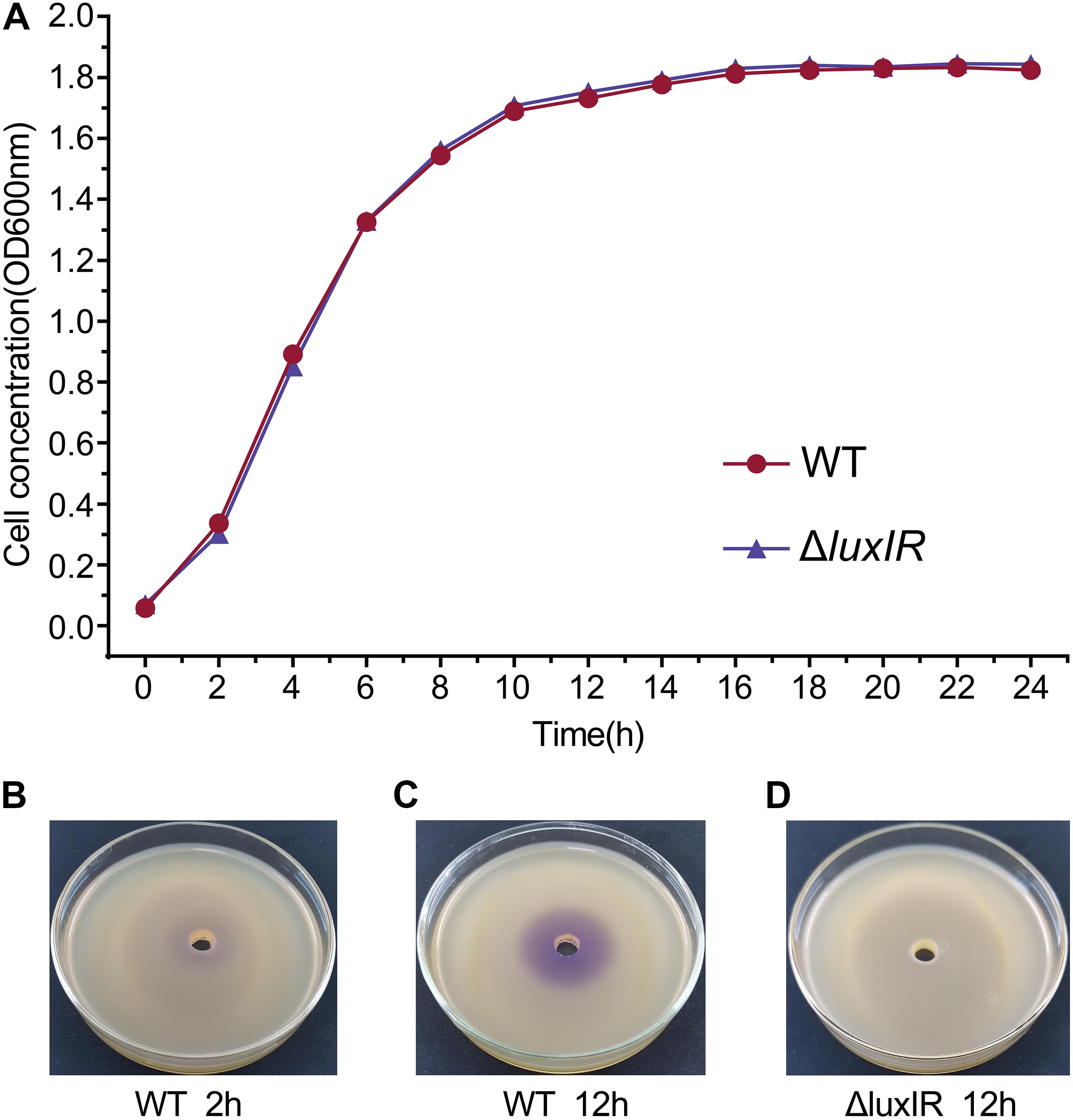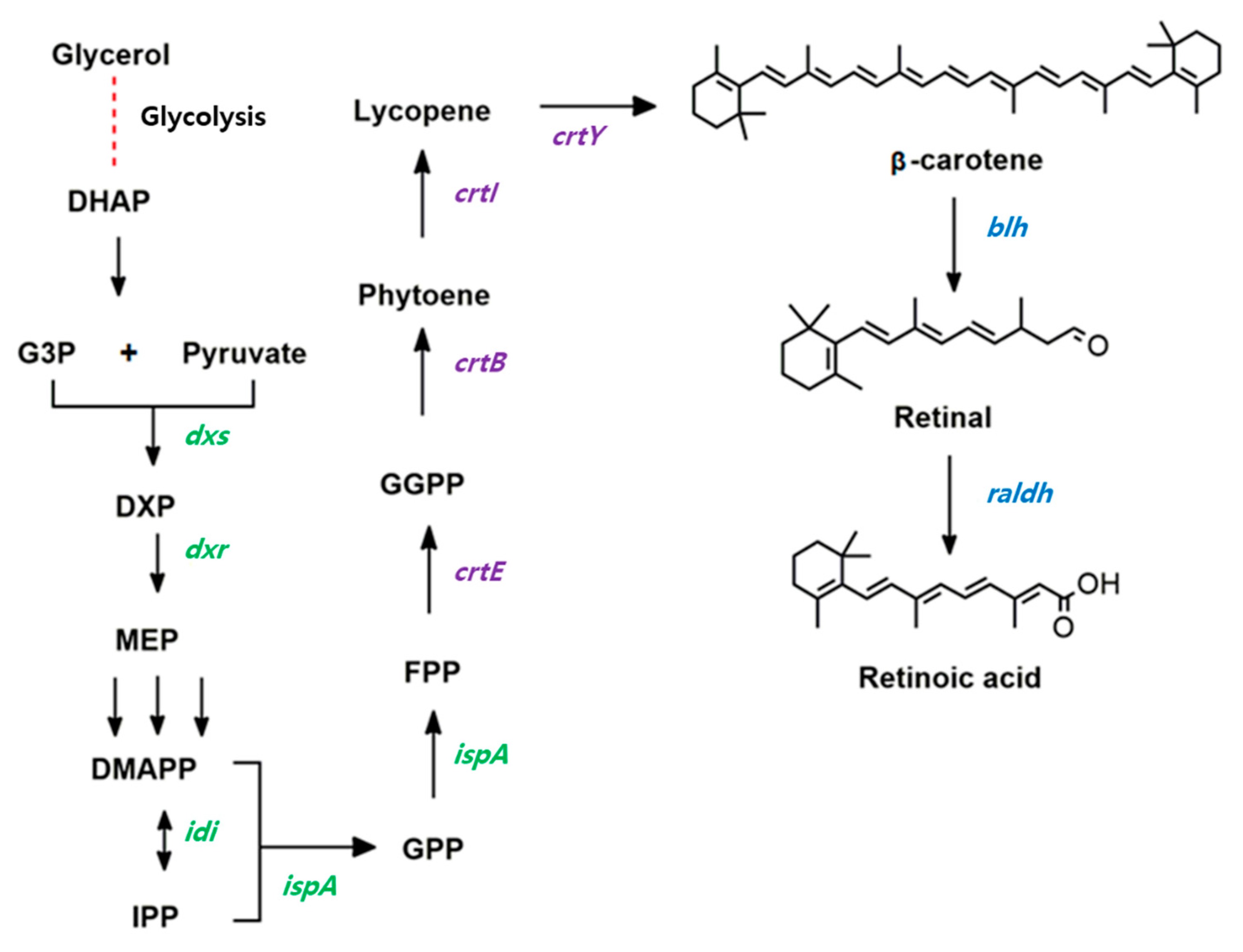
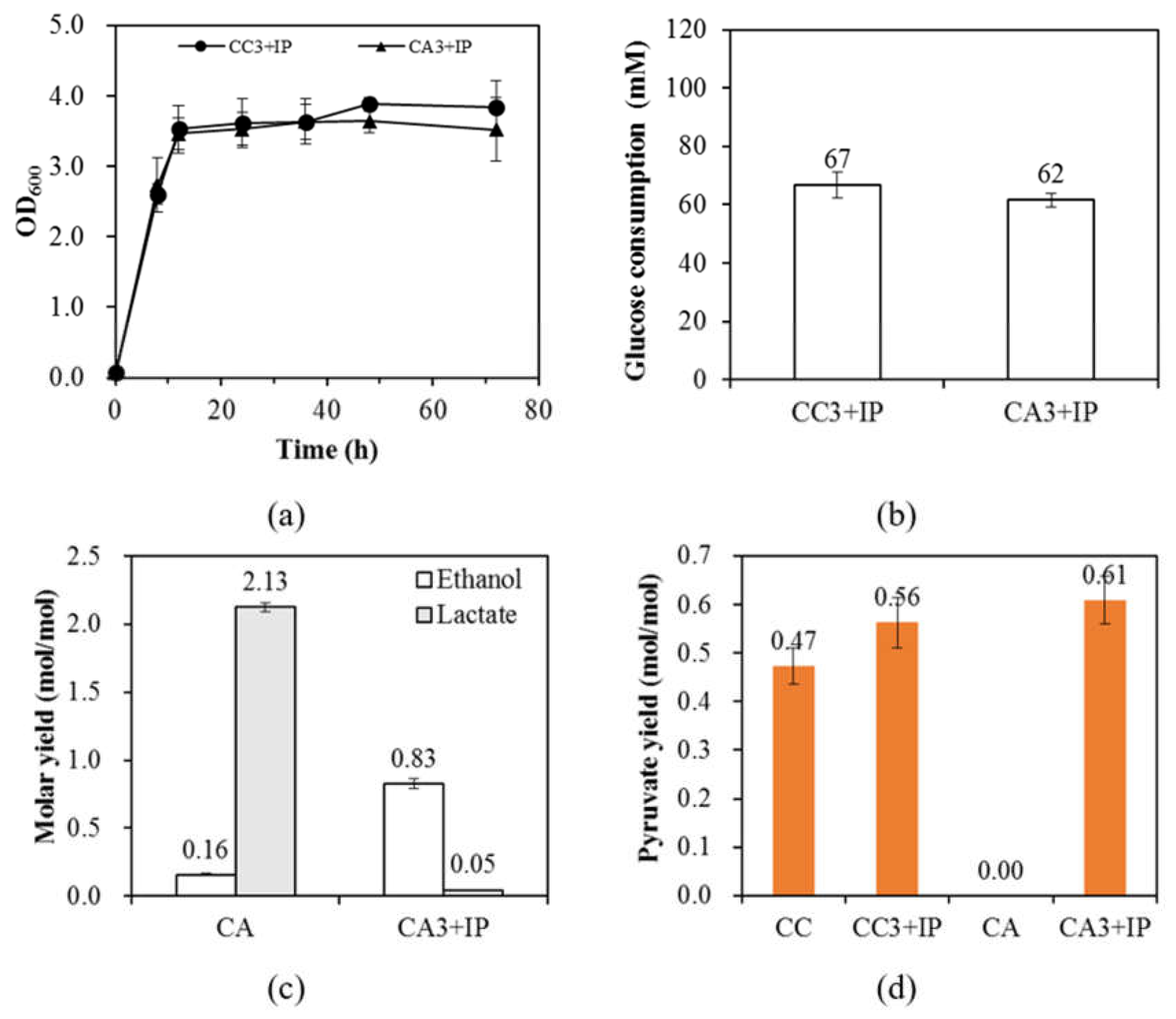
Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | Microbial Production of Bioactive Retinoic Acid Using Metabolically Engineered Escherichia coli
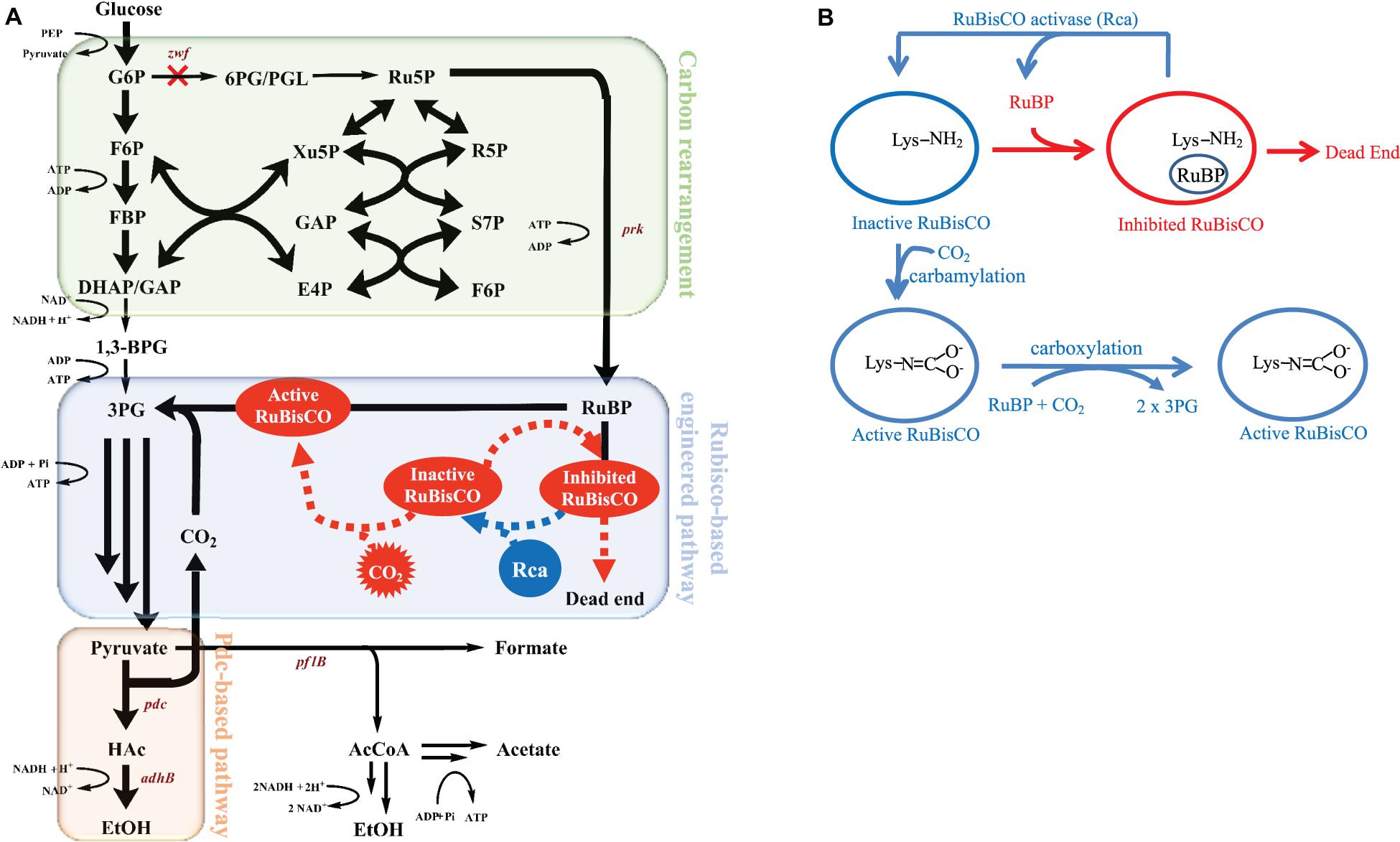
Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | The Physiological Responses of Escherichia coli Triggered by Phosphoribulokinase (PrkA) and Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase (Rubisco)

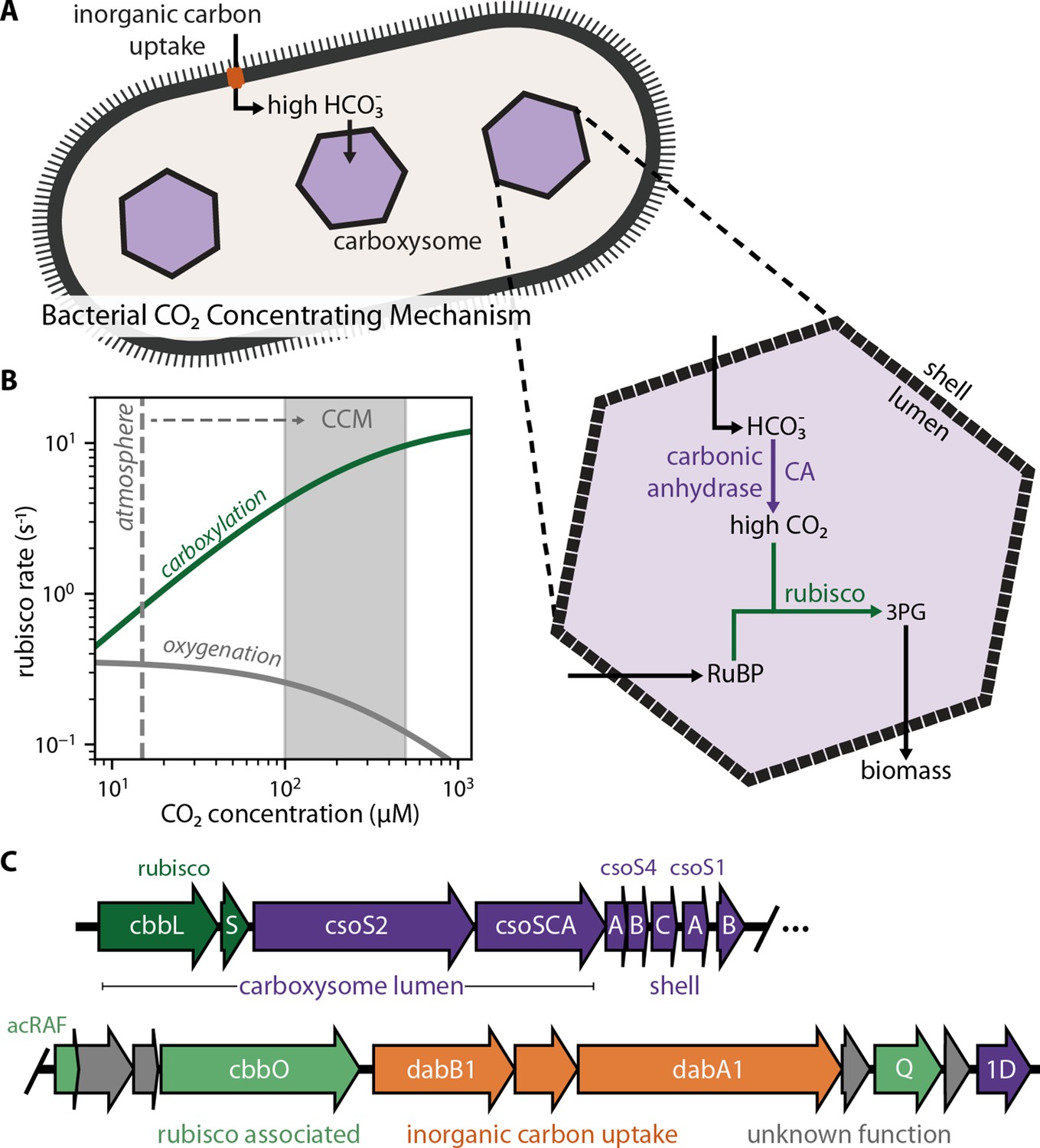
Auxiliary Module Promotes the Synthesis of Carboxysomes in E. coli to Achieve High-Efficiency CO2 Assimilation | ACS Synthetic Biology
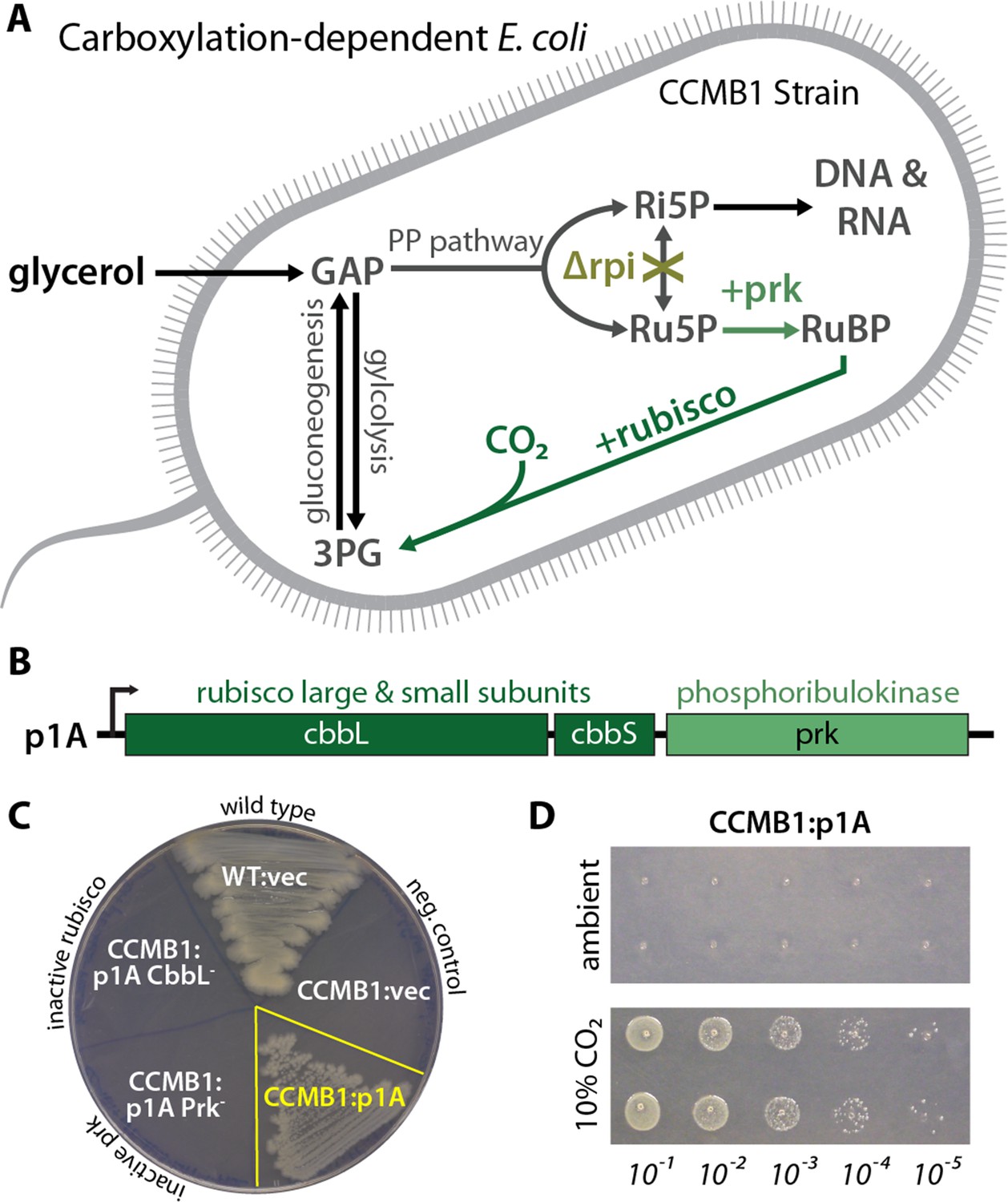
Expression and Assembly of Active Cyanobacterial Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase in Escherichia coli Containing

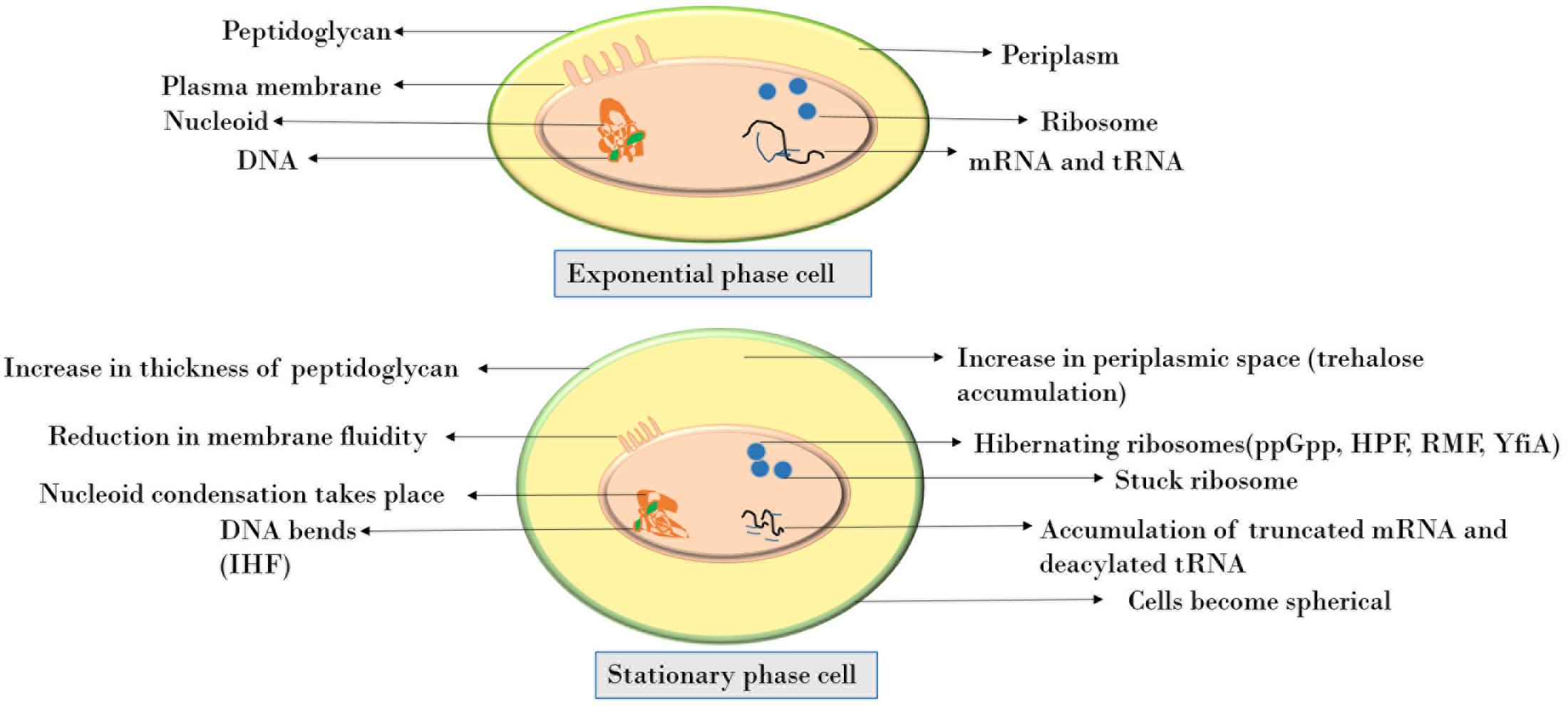
Defining the impact of exoribonucleases in the shift between exponential and stationary phases | Scientific Reports

Exogenous carbon monoxide suppresses Escherichia coli vitality and improves survival in an Escherichia coli-induced murine sepsis model | Acta Pharmacologica Sinica
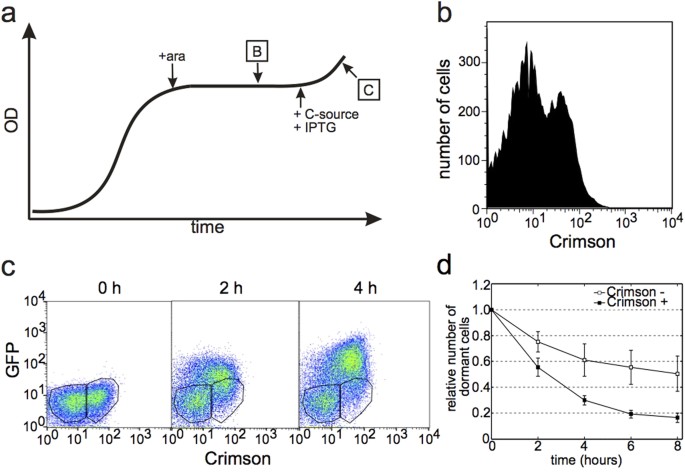
Growth resumption from stationary phase reveals memory in Escherichia coli cultures | Scientific Reports

Highly Efficient Biosynthesis of Heliotropin by Engineered Escherichia coli Coexpressing Trans-Anethole Oxygenase and Formate Dehydrogenase | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry

Bacterial respiration during stationary phase induces intracellular damage that leads to delayed regrowth - ScienceDirect
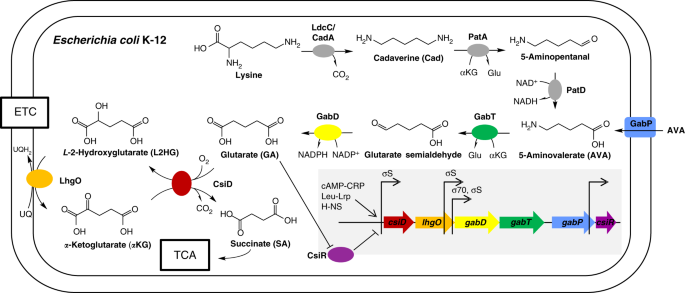
Widespread bacterial lysine degradation proceeding via glutarate and L-2-hydroxyglutarate | Nature Communications

Bacterial respiration during stationary phase induces intracellular damage that leads to delayed regrowth - ScienceDirect
Escherichia coli Response to Uranyl Exposure at Low pH and Associated Protein Regulations | PLOS ONE

Antioxidants | Free Full-Text | Effects of the Quinone Oxidoreductase WrbA on Escherichia coli Biofilm Formation and Oxidative Stress
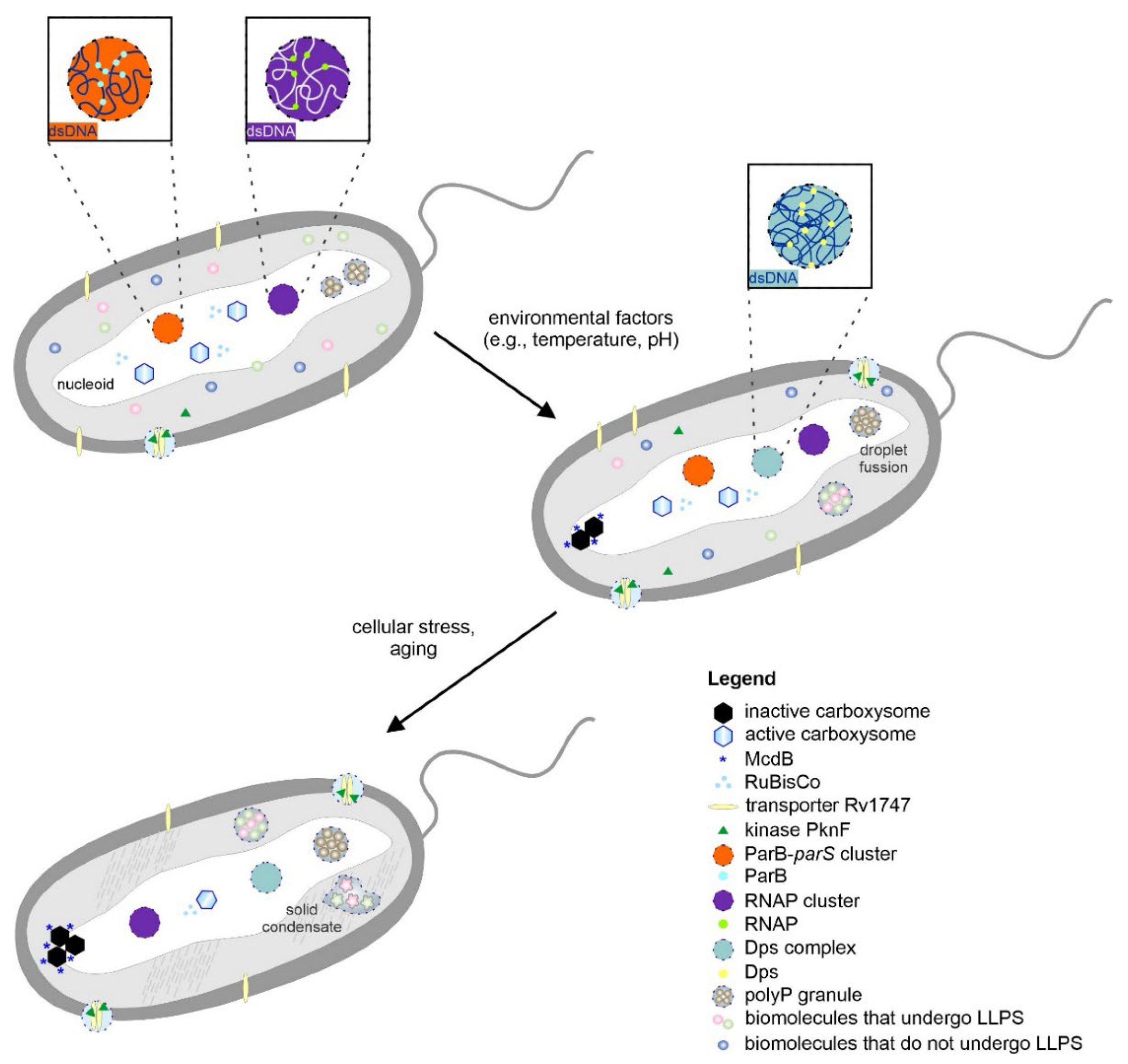
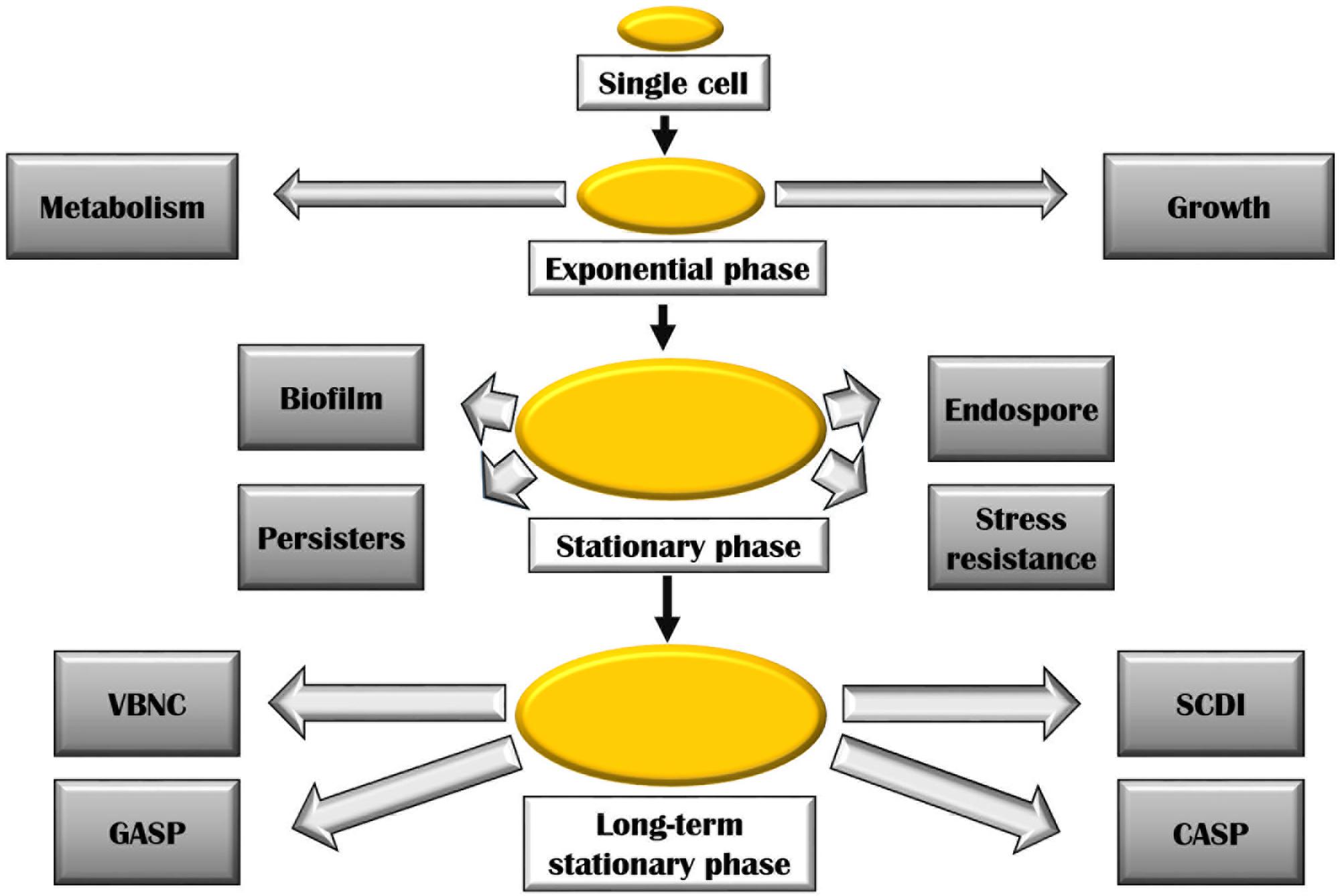
Biomolecules | Free Full-Text | Getting Closer to Decrypting the Phase Transitions of Bacterial Biomolecules